Deployment Troubleshooting
Deployment Troubleshooting
Problem: You’re encountering errors during LangFuse deployment or post-deployment configuration.
Solution: This comprehensive troubleshooting guide covers the most common deployment issues with specific solutions based on real deployment experience.
Quick Fix: Most Azure deployment issues are timing-related and resolve with a simple retry after waiting 30-60 seconds.
Database-Specific Issues: For ClickHouse replication problems, ZooKeeper coordination issues, or Bitnami registry migration errors, see the dedicated ClickHouse Troubleshooting Guide.
Common Deployment Issues
Permission Errors
Error Pattern: StatusCode=403 or permission-related failures
Key Vault Certificate Permissions
Error: Status=403 Code="Forbidden" Message="The user, group or application ... does not have certificates get/delete permission on key vault"
Root Cause: This occurs when:
- Terraform needs to create/recreate/update certificates
- The service principal lacks certificate management permissions
- Key Vault RBAC model requires explicit permission assignment
- New Key Vault created without proper access policies
Universal Solution:
# Get the Key Vault name from current deployment
KEYVAULT_NAME=$(terraform show -json | jq -r '.values.root_module.child_modules[] | select(.address=="module.langfuse") | .resources[] | select(.type=="azurerm_key_vault") | .values.name')
# Add all certificate permissions to current user
az keyvault set-policy --name $KEYVAULT_NAME --upn $(az account show --query user.name -o tsv) \
--certificate-permissions create delete get list update import backup restore recover purge
# Verify permissions were added
az keyvault show --name $KEYVAULT_NAME --query "properties.accessPolicies[?objectId=='$(az ad user show --id $(az account show --query user.name -o tsv) --query objectId -o tsv)'].permissions.certificates"Alternative: Manual Permission Assignment
# If the above doesn't work, use your specific email
az keyvault set-policy --name your-keyvault-name --upn your-email@justice.gov.uk \
--certificate-permissions create delete get list update import backup restore recover purgeAfter Adding Permissions:
sleep 30
terraform apply -auto-approveGeneral Permission Propagation
Error: Various StatusCode=403 errors
Root Cause: Azure permissions take time to propagate across services
Solution: Wait for 30-60 seconds and retry.
Key Vault Issues
Soft-Delete Conflicts
Error: Vault name 'your-vault-name' is already in use or similar naming conflicts
Root Cause: Azure Key Vault has soft-delete enabled by default. When Terraform recreates a Key Vault (e.g., due to domain changes), the old vault enters a “soft-deleted” state for 7 days.
Prevention: Before changing domains that affect Key Vault names:
# 1. Get current Key Vault name from Terraform state
CURRENT_VAULT=$(terraform show -json | jq -r '.values.root_module.child_modules[] | select(.address=="module.langfuse") | .resources[] | select(.type=="azurerm_key_vault") | .values.name')
# 2. Delete the Key Vault before applying changes
az keyvault delete --name $CURRENT_VAULT --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>
# 3. Check for any soft-deleted conflicts
az keyvault list-deleted --subscription $(az account show --query id -o tsv)
# 4. Apply Terraform changes
terraform apply -auto-approvePost-Conflict Resolution: If you encounter the error after deployment:
# Check for soft-deleted vaults
az keyvault list-deleted --subscription $(az account show --query id -o tsv)
# If there's a naming conflict, either:
# Option 1: Wait 7 days for automatic purge
# Option 2: Change your domain/name to avoid conflict
# Option 3: Use different random suffix (remove from state)
terraform state rm module.langfuse.random_string.key_vault_postfix
terraform apply -auto-approveKey Vault Recovery Issues
Error: Vault name 'your-vault-name' is already in use
Solution 1: Force new Key Vault name
terraform state rm module.langfuse.random_string.key_vault_postfix
terraform applySolution 2: Purge existing vault
az keyvault purge --name your-vault-name --location westeuropeNaming and Resource Conflicts
Resource Already Exists
Error: name.*already exists or similar conflicts
Root Cause: Resource names must be globally unique or conflict with soft-deleted resources
Solution: Use different names or clean up existing resources
# Check for existing resources
az resource list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --output table
# Delete conflicting resources if safe
az resource delete --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --name conflicting-resource-name --resource-type Microsoft.KeyVault/vaultsApplication Gateway Issues
Redirect Configuration Conflicts
Error: ConflictError.*redirectConfigurations or AGIC-related errors
Root Cause: Application Gateway Ingress Controller (AGIC) configuration conflicts
Solution: Refresh and reapply
terraform refresh
terraform apply -auto-approveBackend Health Issues
Error: 502 Bad Gateway errors
Root Cause: Multiple possible causes require systematic diagnosis to identify the specific issue.
Diagnostic Approach: Use the branching strategy below to identify your specific 502 error type.
502 Bad Gateway Error Types - Summary
Based on real deployment experience, we’ve identified 5 distinct types of 502 Bad Gateway errors:
| Type | Symptoms | Root Cause | Resolution Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: Pod Startup Failure | Pods not running (Pending, CrashLoopBackOff) | Resource constraints, config errors | 10-30 minutes |
| B: Backend IP Mismatch | Backend “Unhealthy”, pods running | Pods restarted, gateway not updated | 5 minutes |
| C: AGIC Configuration Issue | Backend “Healthy” but still 502 | AGIC config conflicts | 15 minutes |
| D: AGIC Permission Issue | AGIC logs show “authorizationfailed” | Missing permissions | 10 minutes |
| E: ZooKeeper Memory Exhaustion | UI shows null traces, AKS OOM logs | ZooKeeper memory exhaustion | 30-60 minutes |
502 Error Diagnostic Tree
Step 1: Check Pod Status
kubectl get pods -n langfuseIf pods are not running (Pending, CrashLoopBackOff, etc.): - → Type A: Pod Startup Failure (see below)
If pods are running, continue to Step 2:
Step 2: Check Application Gateway Backend Health
az network application-gateway show-backend-health --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY>If backend shows “Unhealthy”: - → Type B: Backend IP Mismatch (see below)
If backend shows “Healthy” but still getting 502: - → Type C: AGIC Configuration Issue (see below)
Step 3: Check AGIC Logs
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment/ingress-appgw-deployment | grep -i "authorizationfailed" | tail -5If permission errors found: - → Type D: AGIC Permission Issue (see below)
Type A: Pod Startup Failure
Symptoms: Pods in Pending, CrashLoopBackOff, or other non-Running states
Root Cause: Resource constraints, configuration errors, or infrastructure issues
Resolution:
# Check pod events for specific errors
kubectl describe pods -n langfuse
# Check resource usage
kubectl top pods -n langfuse
# Check node resources
kubectl describe nodes
# If resource constraints, scale AKS node pool
# Update node_pool_max_count in main.tf and reapplyType B: Backend IP Mismatch
Symptoms: Backend shows “Unhealthy”, pods are running but gateway points to wrong IP
Root Cause: LangFuse pods restarted and got new IP addresses, but Application Gateway wasn’t updated
Quick Fix (5 minutes):
# 1. Get current pod IP
POD_IP=$(kubectl get pods -n langfuse -o wide | grep langfuse-web | awk '{print $6}')
# 2. Update Application Gateway backend pool
az network application-gateway address-pool update \
--gateway-name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY> \
--resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> \
--name pool-langfuse-langfuse-web-http-bp-3000 \
--servers $POD_IP
# 3. Test the website
curl -k -I https://<YOUR_DOMAIN>Permanent Fix (One-time setup):
# Grant AGIC permission to auto-update backend IPs
RESOURCE_GROUP="<YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>"
AGIC_CLIENT_ID=$(kubectl get configmap ingress-appgw-cm -n kube-system -o jsonpath='{.data.AZURE_CLIENT_ID}')
AGIC_OBJECT_ID=$(az ad sp show --id $AGIC_CLIENT_ID --query id -o tsv)
SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(az account show --query id -o tsv)
az role assignment create \
--assignee $AGIC_OBJECT_ID \
--role "Contributor" \
--scope "/subscriptions/$SUBSCRIPTION_ID/resourceGroups/$RESOURCE_GROUP"
kubectl rollout restart deployment ingress-appgw-deployment -n kube-system
sleep 45Type C: AGIC Configuration Issue
Symptoms: Backend shows “Healthy” but still getting 502, AGIC logs show configuration errors
Root Cause: AGIC configuration conflicts or corrupted state
Resolution:
# 1. Refresh Terraform state
terraform refresh
# 2. Reapply configuration
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 3. Restart AGIC to pick up changes
kubectl rollout restart deployment ingress-appgw-deployment -n kube-system
# 4. Wait for restart and verify
sleep 45
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment/ingress-appgw-deployment --tail=10Type D: AGIC Permission Issue
Symptoms: AGIC logs show “authorizationfailed” or permission errors
Root Cause: AGIC managed identity lacks required permissions
Resolution:
# 1. Get AGIC managed identity details
AGIC_CLIENT_ID=$(kubectl get configmap ingress-appgw-cm -n kube-system -o jsonpath='{.data.AZURE_CLIENT_ID}')
AGIC_OBJECT_ID=$(az ad sp show --id $AGIC_CLIENT_ID --query id -o tsv)
# 2. Grant Contributor permissions
az role assignment create \
--assignee $AGIC_OBJECT_ID \
--role "Contributor" \
--scope "/subscriptions/$(az account show --query id -o tsv)/resourceGroups/<YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>"
# 3. Restart AGIC
kubectl rollout restart deployment ingress-appgw-deployment -n kube-system
sleep 45Type E: ZooKeeper Memory Exhaustion
Symptoms: Multiple components failing, memory issues, cascading failures, persistent 502 errors
Root Cause: ZooKeeper memory exhaustion triggering cascading failures across ClickHouse, StatefulSets, and Application Gateway
Visual Indicators of ZooKeeper OOM Issues
LangFuse UI Symptoms
When ZooKeeper memory exhaustion occurs, the LangFuse UI may show degraded functionality:
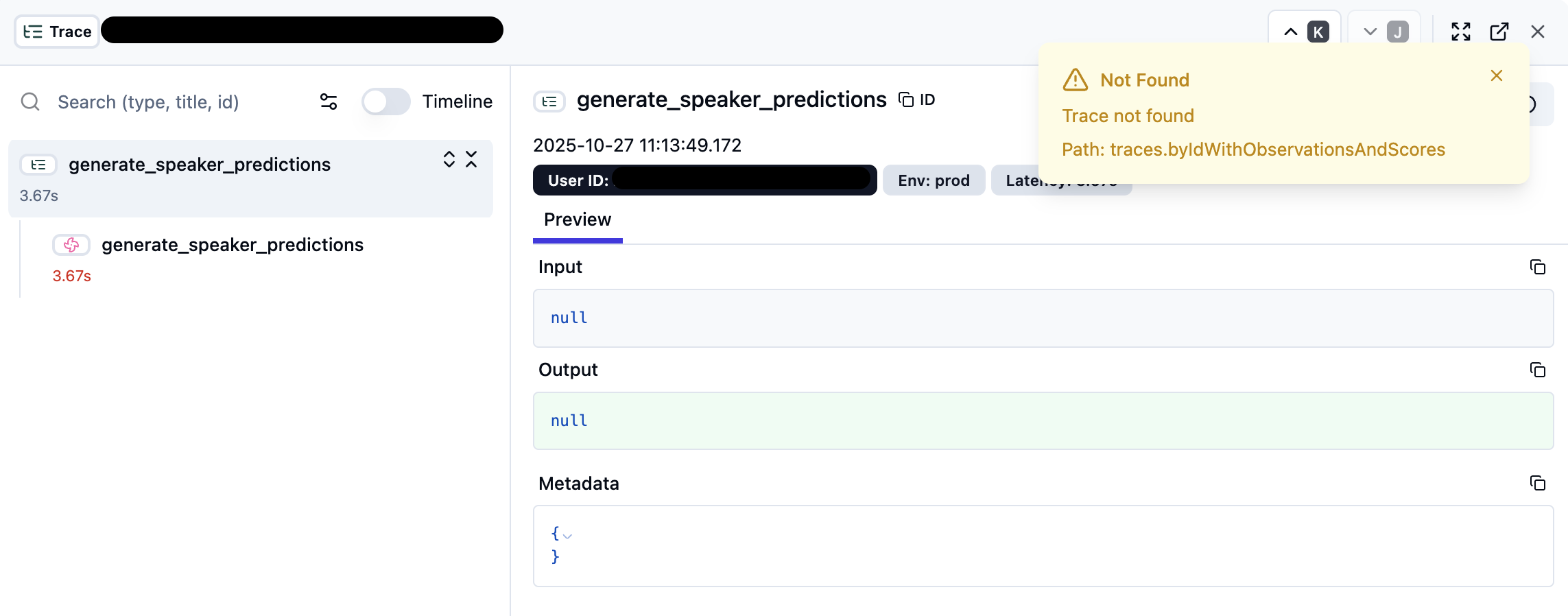
Key UI Indicators:
- Trace Loading Issues: Traces may show “Not Found” errors or fail to load completely
- Null Input/Output: Trace data appears as
nullvalues instead of actual content - Empty Metadata: Trace metadata sections show empty JSON objects
{} - Timeline Disruption: Trace timeline may be incomplete or missing spans
AKS Monitor Symptoms
Critical Error Pattern in AKS Logs:
Memory cgroup out of memory: Killed process ...Key Log Indicators:
- “Memory cgroup out of memory” - Primary OOM signal
- “Killed process” - Process termination due to memory limits
- High oom_score_adj values - Indicates container memory pressure
Diagnostic Steps:
# Check for OOMKilled containers
kubectl describe pods -n langfuse | grep -A 5 -B 5 "OOMKilled"
# Monitor memory usage
kubectl top pods -n langfuse
# Check ZooKeeper logs specifically
kubectl logs -n langfuse statefulset/langfuse-zookeeper --tail=100
# Search AKS logs for OOM events
kubectl get events -n langfuse --field-selector reason=OOMKilling
# Check container memory limits vs usage
kubectl describe pod -n langfuse -l app.kubernetes.io/name=zookeeperResolution:
# 1. Check current ZooKeeper memory allocation
kubectl get statefulset langfuse-zookeeper -n langfuse -o yaml | grep -A 5 resources
# 2. Increase ZooKeeper memory via Helm upgrade
helm upgrade langfuse bitnami/langfuse -n langfuse \
--set zookeeper.resources.limits.memory=1Gi \
--set zookeeper.resources.requests.memory=512Mi
# 3. Restore StatefulSet configuration if corrupted
helm upgrade langfuse bitnami/langfuse -n langfuse \
--set zookeeper.auth.enabled=false \
--set zookeeper.allowAnonymousLogin=true
# 4. Fix Application Gateway backend configuration
POD_IP=$(kubectl get pods -n langfuse -o wide | grep langfuse-web | awk '{print $6}')
az network application-gateway address-pool update \
--gateway-name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY> \
--resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> \
--name pool-langfuse-langfuse-web-http-bp-3000 \
--servers $POD_IP
# 5. Verify resolution
kubectl get pods -n langfuse
kubectl top pods -n langfuse
curl -I https://<YOUR_DOMAIN>Prevention:
# Set up resource monitoring
kubectl top pods -n langfuse --watch
# Monitor specific memory usage
watch -n 10 'kubectl top pods -n langfuse | grep zookeeper'Diagnostic Steps:
# Check AKS pods
kubectl get pods -n langfuse
# Check ingress configuration
kubectl get ingress -n langfuse -o yaml
# Check Application Gateway backend health
az network application-gateway show-backend-health --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY>
# Check for permission errors in the gateway controller
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment/ingress-appgw-deployment | grep -i "authorizationfailed" | tail -5DNS and SSL Issues
DNS Propagation Delays
Problem: Domain not resolving after deployment
Solution: Wait and verify DNS propagation
# Test NS delegation
nslookup -type=NS <YOUR_DOMAIN>
# Test A record resolution
nslookup <YOUR_DOMAIN>
# Wait 5-30 minutes for global propagationSSL Certificate Issues
Problem: Browser shows “Not Secure” or certificate warnings
Root Cause: After restarting the gateway controller, it forgets to use the Let’s Encrypt certificate and falls back to the self-signed one stored in Azure Key Vaultthat browsers don’t trust.
Quick Fix (5 minutes):
# 1. Remove the old certificate configuration
kubectl patch ingress langfuse -n langfuse --type='json' -p='[{"op": "remove", "path": "/metadata/annotations/appgw.ingress.kubernetes.io~1appgw-ssl-certificate"}]'
# 2. Tell it to use the proper Let's Encrypt certificate
kubectl patch ingress langfuse -n langfuse --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/tls", "value": [{"hosts": ["<YOUR_DOMAIN>"], "secretName": "langfuse-tls-secret"}]}]'
# 3. Wait for the change to take effect (60 seconds)
sleep 60
# 4. Test the website
curl -I https://<YOUR_DOMAIN>Permanent Fix (One-time setup):
# Check if the certificate is properly configured
kubectl get certificate langfuse-tls -n langfuseIf it shows “Ready: True”, the certificate is working. If not, you may need to reapply the SSL configuration. See the SSL Certificates Guide
Diagnostic Steps:
# Check certificate configuration
kubectl get certificate -n langfuse
# Check ingress TLS configuration
kubectl get ingress langfuse -n langfuse -o yaml | grep -A 5 tls
# Test SSL certificate
openssl s_client -connect <YOUR_DOMAIN>:443 -servername <YOUR_DOMAIN>
# Check SSL certificate issuer
openssl s_client -connect <YOUR_DOMAIN>:443 -servername <YOUR_DOMAIN> </dev/null 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -text | grep -A 1 "Issuer:"SMTP Email Delivery Issues
Problem Symptom
Issue: Emails appear to send successfully from LangFuse UI (user invitations, password resets) but recipients never receive them.
- ✅ No error shown in LangFuse interface
- ✅ “Invitation sent” message appears
- ❌ Email never arrives in recipient’s inbox (including spam folder)
Root Cause Investigation
Step 1: Check LangFuse Web Logs
The real issue will be visible in the application logs:
# Check recent logs for SMTP authentication errors
kubectl logs -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web --tail=100 --since=30m | grep -E "(535|SMTP|authentication|mail)"Expected Error Pattern:
Error Invalid login: 535 5.7.3 Authentication unsuccessfulStep 2: Verify Current SMTP Configuration
Check what SMTP credentials are actually being used:
# Get current SMTP configuration from running pod
kubectl exec -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web -- printenv SMTP_CONNECTION_URL
# Expected format: smtp://resource.appId.tenantId:clientSecret@smtp.azurecomm.net:587/...Fix: Credential Mismatch Resolution
Problem: Wrong Client Secret
The most common cause is using an expired or incorrect client secret in the SMTP connection string.
Solution Steps:
1. Get Current App Registration Client Secret - Go to Azure Portal → App Registrations - Find your SMTP app (e.g., langfuse-smtp-app) - Go to “Certificates & secrets” - Note the current valid client secret value
2. Check App Registration ID
# Verify the app registration exists and get its details
kubectl exec -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web -- printenv SMTP_CONNECTION_URL | sed 's/.*:\/\/[^.]*\.\([^.]*\)\..*/App ID: \1/'
# Cross-reference with Azure Portal app registration3. Update SMTP Configuration with Correct Secret
# Replace with actual values from your Azure Portal
kubectl set env deployment/langfuse-web -n langfuse \
SMTP_CONNECTION_URL="smtp://langfuse-ai-smtp.YOUR_APP_ID.YOUR_TENANT_ID:YOUR_CORRECT_CLIENT_SECRET@smtp.azurecomm.net:587/?pool=true&secure=false&requireTLS=true"4. Wait for Pod Restart
kubectl rollout status deployment/langfuse-web -n langfuse --timeout=120sRequired SMTP Configuration Format
For Azure Communication Services SMTP authentication:
Username: <ACS_resource_name>.<Entra_app_client_ID>.<Tenant_ID>
Password: <Entra_app_client_secret>
Server: smtp.azurecomm.net
Port: 587 (STARTTLS)Critical Points:
- Use dots (
.) as separators in username, not pipes (|) - Password must be the current Entra app client secret, not ACS access key
- Client secret must be from the same app registration used in the username
Testing and Verification
Verify SMTP Fix
After updating credentials:
# Check for new authentication errors (should be none)
kubectl logs -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web --since=5m | grep -E "(535|authentication)" || echo "No SMTP errors found"
# Test email from LangFuse UI
# Send user invitation and check logs for successConfiguration Maintenance
After Helm Upgrades
Environment variables set with kubectl set env may be overwritten by Helm. After Helm operations, re-verify:
# Check if SMTP config is still correct
kubectl exec -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web -- printenv SMTP_CONNECTION_URL
# If reverted, reapply the correct configurationClient Secret Rotation
When rotating Azure AD app registration secrets:
- Generate new client secret in Azure Portal
- Update SMTP_CONNECTION_URL with new secret using
kubectl set env - Ensure old secret is deleted only after confirming new one works
Quick Diagnostic Checklist
AKS and Kubernetes Issues
Pod Startup Failures
Problem: LangFuse pods not starting
Diagnostic Steps:
# Check pod status
kubectl get pods -n langfuse
# Check pod logs
kubectl logs -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web --tail=50
# Check events
kubectl get events -n langfuse --sort-by='.lastTimestamp'Resource Constraints
Problem: Pods pending or resource-related errors
Solution: Check and adjust resources
# Check node resources
kubectl describe nodes
# Check resource quotas
kubectl describe resourcequota -n langfuse
# Scale nodes if needed (via Terraform)
# Update node_pool_max_count in main.tfSystematic Troubleshooting Approach
1. Check Current State
# Verify Azure login and subscription
az account show
# Check resource group
az group show --name <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>
# List all resources
az resource list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --output table
# Check LangFuse pods and database components
kubectl get pods -n langfuse
kubectl get statefulset -n langfuse2. Validate Terraform State
# Check Terraform state
terraform show
# Validate configuration
terraform validate
# Plan to see differences
terraform plan3. Monitor Resource Creation
# Watch resource creation in real-time
watch -n 5 'az resource list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --query "[].{Name:name,Type:type,Status:provisioningState}" --output table'
# Monitor specific resources
watch -n 5 'az keyvault show --name your-vault-name --query "properties.provisioningState"'4. Emergency Recovery
# Reset problematic resources
terraform state rm module.langfuse.azurerm_key_vault.this
terraform apply -auto-approve
# Force resource recreation
terraform taint module.langfuse.azurerm_application_gateway.this
terraform apply -auto-approveError Pattern Reference
| Error Pattern | Common Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
StatusCode=403 |
Permission not propagated | Wait 30-60 seconds, retry |
certificates delete permission |
Missing Key Vault permissions | Add certificate permissions via az keyvault set-policy |
Vault name.*already in use |
Key Vault soft-delete conflict | Delete old Key Vault before domain changes |
name.*already exists |
Resource name collision | Use different name or clean up existing |
Cannot import non-existent |
Import block referencing deleted resource | Remove import block |
exceeds.*character limit |
Name too long | Use shorter name parameter |
MethodNotAllowed.*Purge |
Purge protection enabled | Use different name or disable protection |
ConflictError.*already in use |
Soft-deleted resource | Purge or use different name |
InvalidResourceReference.*redirectConfigurations |
AGIC configuration conflict | Run terraform refresh, then apply |
| 502 Bad Gateway | Multiple possible causes | Use diagnostic tree to identify specific type (see 502 Error Types Summary) |
| “Your connection is not private” | Wrong SSL certificate being used | Switch to Let’s Encrypt certificate (see SSL Certificate Issues) |
| Gateway shows “Unhealthy” | Server IP mismatch or server not responding | Type B: Backend IP Mismatch (see above) |
| Permission errors in logs | Gateway controller can’t update settings | Type D: AGIC Permission Issue (see above) |
| 535 5.7.3 Authentication unsuccessful | SMTP client secret mismatch | Update SMTP_CONNECTION_URL with correct client secret (see SMTP Email Delivery Issues) |
| Emails not delivered but no UI errors | SMTP authentication failing silently | Check LangFuse logs for SMTP errors (see SMTP Email Delivery Issues) |
| “Same provider” SSO error | Existing password-based user blocks SSO | Delete user record to allow fresh SSO setup (see User Management Guide) |
| Inconsistent UI data on refresh | ClickHouse replica UUID mismatch | See ClickHouse Troubleshooting Guide |
| ImagePullBackOff with bitnami images | Bitnami registry migration (Aug 2025) | Use bitnamilegacy registry (see ClickHouse Troubleshooting Guide) |
| ZooKeeper OOM errors | Memory exhaustion in coordination layer | Increase ZooKeeper memory limits (see ClickHouse Troubleshooting Guide) |
Comprehensive Troubleshooting Reference
Quick Diagnosis Commands
When something goes wrong, check these in order:
# 1. Are all the LangFuse services running?
kubectl get pods -n langfuse
# 2. Is the gateway pointing to the right server?
az network application-gateway show-backend-health --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY>
# 3. Are there any permission errors in the gateway controller?
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment/ingress-appgw-deployment | grep -i "authorizationfailed" | tail -5
# 4. Is the SSL certificate working?
openssl s_client -connect <YOUR_DOMAIN>:443 -servername <YOUR_DOMAIN> </dev/null 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -text | grep -A 1 "Issuer:"
# 5. Are emails failing to send (SMTP issues)?
kubectl logs -n langfuse deployment/langfuse-web --tail=100 --since=30m | grep -E "(535|SMTP|authentication|mail)"Discovery Commands
Need to find the correct values for your deployment?
# Find your resource groups
az group list --query "[?contains(name, 'langfuse') || contains(name, 'lng')].name" -o tsv
# Find your Application Gateway
az network application-gateway list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --query "[].{Name:name, ProvisioningState:provisioningState}" -o table
# Find your AKS cluster
az aks list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --query "[].{Name:name, ResourceGroup:resourceGroup}" -o table
# Get AGIC managed identity details
kubectl get configmap ingress-appgw-cm -n kube-system -o yaml | grep AZURE_CLIENT_ID
# Get AGIC managed identity object ID
AGIC_CLIENT_ID=$(kubectl get configmap ingress-appgw-cm -n kube-system -o jsonpath='{.data.AZURE_CLIENT_ID}')
az ad sp show --id $AGIC_CLIENT_ID --query "{DisplayName:displayName, ObjectId:id, ClientId:appId}" -o table
# Check current role assignments for AGIC
AGIC_OBJECT_ID=$(az ad sp show --id $AGIC_CLIENT_ID --query id -o tsv)
az role assignment list --assignee $AGIC_OBJECT_ID --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>Health Check Commands
One command to check if everything is working:
# This will show you the status of all components
echo "=== Pod Status ===" && kubectl get pods -n langfuse && \
echo "=== Gateway Health ===" && az network application-gateway show-backend-health --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --name <YOUR_APP_GATEWAY> | jq '.backendAddressPools[0].backendHttpSettingsCollection[0].servers[0].health' && \
echo "=== Website Response ===" && curl -k -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" https://<YOUR_DOMAIN>Best Practices for Troubleshooting
1. Incremental Deployment
For complex deployments, use targeted applies:
# Deploy infrastructure first
terraform apply -target="module.langfuse.azurerm_resource_group.this"
terraform apply -target="module.langfuse.azurerm_virtual_network.this"
# Then security resources
terraform apply -target="module.langfuse.azurerm_key_vault.this"
sleep 60
# Finally application resources
terraform apply2. Resource Monitoring
# Monitor deployment progress
az resource list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> \
--query "[?provisioningState!='Succeeded'].{Name:name,State:provisioningState}" \
--output table3. Log Collection
# Collect deployment logs
terraform apply -auto-approve 2>&1 | tee deployment.log
# Collect Azure CLI debug info
az resource list --resource-group <YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP> --debug 2>&1 | tee azure-debug.logComplex Multi-Component Failures
Note: For ZooKeeper memory exhaustion issues that present as 502 Bad Gateway errors, see Type E: ZooKeeper Memory Exhaustion in the Application Gateway Issues section above.
🔧 Most deployment issues are temporary and resolve with patience and systematic troubleshooting.